| ANTIMONY POTASSIUM TARTRATE
TRIHYDRATE
|
||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 11071-15-1
(Anhydrous) 28300-74-5 (Trihydrate) |
|
| EINECS NO. | 234-293-3 | |
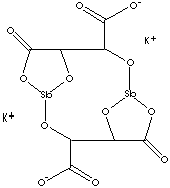
| FORMULA | K2[Sb2(C4H4O6)2]·3H2O | |
| MOL WT. | 667.86 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
||
| SMILES |
|
|
| TOXICITY | ||
| SYNONYMS | Tartar Emetic; | |
| Tartaric acid, antimony potassium salt, trihydrate; Potassium antimony(III) oxide tartrate hemihydrate; Dipotassium bis[mu-[tartrato(4-)-O1,O2:O3, O4]] diantimonate(2-); Bis[.mu.-[tartrato(4-)-O1,O2:O3,O4]]diantimonato(2-) de dipotasio (Spanish); | ||
| SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white crystalline powder | |
| MELTING POINT | 332 - 335 C (Decomposes) | |
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 2.6 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | moderately soluble (soluble in glycerine, insoluble in EtOH) | |
| pH | 3.5 - 4.5 (solution) | |
| NFPA RATING | Health: 3; Flammability: 0; Reactivity: 0 | |
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
| FLASH POINT |
|
|
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||
|
Antimony Potassium Tartrate is used as a mordant or fixing agent in the leather and textile dying as well as an analytical reagent and a flux additive for electoplating. It is used in making insecticides or pesticides. It was used as a parasiticide or as an emetic and expectorant. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white crystals | |
| CONTENT |
98.0% min |
|
|
LOSS ON DRYING |
3.0% max |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 25kgs in bag | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 6.1 (Packing Group: III) | |
| UN NO. | 1551 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| European Hazard Symbols: XN N, Risk Phrases: 20/22-51/53, Safety Phrases: 61 | ||
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF ANTIMONY AND ITS COMPOUNDS |
||
Antimony is a semi-metallic chemical element in Group Va of the periodic table;
symbol Sb, atomic number 51; atomic mass 121.75; melting point ca 630.7 C; boiling point
at 1,750 C; specific gravity 6.69 at 20 C; valence 0, +3, -3, or +5.;
electronic config. [Kr]4d10 5s2 5p3. There are four allotropic forms. The common
and stable form is a very brittle, blue-white, hexagonal mineral and has a
rhombohedral crystalline structure. Yellow and black antimony shows the
properties of unstable non-metals. It is a poor conductor of heat and
electricity and is easily powdered to be used by itself. The chief ore of
antimony is stibnite (Sb2S3,
antimony trisulfide) which is produced in China and
covers three-fourths of the world's mined antimony. It is also found in
isomorphous mixture with arsenic, as allemonite. Substantial quantity of
antimony are produced as a by-product in the smelting of base metal ores also.
The pure antimony is produced from the ore by roasting it to form the oxide,
then reducing the oxide with carbon or iron. Antimony is soluble in hot nitric
or sulfuric acid and reacts with oxidizing acids and halogens (fluorine,
chlorine, or bromine). It does not react with water at room temperature but will
ignite and burn in air at higher temperatures. To make stronger, brittle,
solidification expanded and low melting point metals, antimony is mixed with
other metals such as lead and zinc alloys which are used in solder, bearings,
castings, safety matches, and as a red pigment in paint as well as as a hardner
in lead storage batteries, the most important use of antimony metal. Antimony is
being the important element in the semiconductor industry to make diodes,
infrared detectors, and Hall-effect devices. Antimony tartrate was used as an
emetic and expectorant, to produce sweating, and treat people infected with
parasites, but is poisonous and has toxic side effects. Mined antimony is
combined with oxygen to form antimony oxide, one of the most important antimony
compounds. Antimony oxide is a white rhombic crystals; melting at 656°C;
insoluble in water; powerful reducing agent. Most antimony oxide produced is
added to textiles and plastics as fire retardant. It is also used in paints,
ceramics and fireworks, and as enamels for plastics, metal and glass. Antimony
oxides don't react as flame retardants directly. They are used as synergists to
enhance the activity of halogenated flame retardants by stepwise releasing the
halogenated radicals to retard gas phase chain reaction of flame spread. There
are many antimony compounds for industrial uses;
|
||